I came across this nifty diagram showing how being inactive contributes to illness. Get moving to stay healthy! When you don't move you gain weight, especially around the middle. White blood cells from your immune system move into the fat around your organs. This ignites inflammation everywhere in your body, which leads to insulin resistance and more weight gain, and ultimately diabetes. This raises your risk for heart disease, high blood pressure and stroke. This inflammation also leads to brain issues like dementia, Parkinsons and Alzheimers. Also increased is your risk for cancer. It is worth saying again. Get moving to protect your health!
Welcome
Who says we have to suffer...to live a healthy happy vibrant life?
Red wine and dark chocolate... might seem decadent...but these guilty pleasures also might help us live longer...and healthier lives. Red wine and dark chocolate definitely improve an evening..but they also contain resveratrol..which lowers blood sugar. Red wine is a great source of catechins..which boost protective HDL cholesterol. Green tea? Protects your brain..helps you live longer..and soothes your spirit.
Food for Thought, the blog, is about living the good life...a life we create with our thoughts and our choices...and having fun the whole while!
I say lets make the thoughts good ones..and let the choices be healthy...exciting...and delicious! Bon Appetit!
Showing posts with label Healthy Heart. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Healthy Heart. Show all posts
Monday, November 12, 2018
Thursday, March 1, 2018
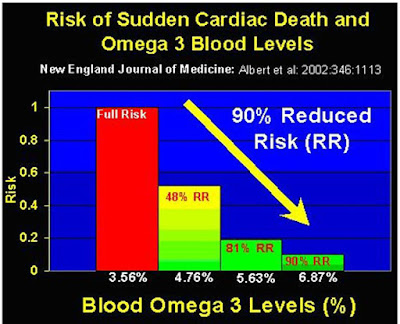
Take your fish oils! To get to a target level you need 1500 to 2000 mg of EPA+DHA daily.
It takes 4 months to raise your Omega-3 Index levels when you begin to increase your dose of EPA and DHA. Shoot for 1500 to 2000 mg of EPA + DHA daily. The image below says it all.
Wednesday, January 31, 2018
Vitamin D3 could heal and protect your heart.
A study has been published in the International Journal of Nanomedicine. It shows that Vitamin D3 -- which is made by the body naturally when skin is exposed to the sun -- can significantly restore the damage to the cardiovascular system caused by several diseases, including hypertension, diabetes and atherosclerosis. Vitamin D3 supplements are also available over-the-counter.
Generally, Vitamin D3 is associated with the bones. However, in recent years, in clinical settings people recognize that many patients who have a heart attack will have a deficiency of D3. It doesn't mean that the deficiency caused the heart attack, but it increased the risk of heart attack. A research team used nanosensors to see why Vitamin D3 can be beneficial, especially for the function and restoration of the cardiovascular system.
The Ohio University team has developed unique methods and systems of measurements using nanosensors, which are about 1,000 times smaller in diameter than a human hair, to track the impacts of Vitamin D3 on single endothelial cells, a vital regulatory component of the cardiovascular system. A major discovery from these studies is that vitamin D3 is a powerful stimulator of nitric oxide (NO), which is a major signaling molecule in the regulation of blood flow and the prevention of the formation of clots in the cardiovasculature. Additionally, vitamin D3 significantly reduced the level of oxidative stress in the cardiovascular system.
Most importantly, these studies show that treatment with vitamin D3 can significantly restore the damage to the cardiovascular system caused by several diseases, including hypertension, atherosclerosis, and diabetes, while also reducing the risk of heart attack. These studies, performed on cells from Caucasian Americans and African Americans, yielded similar results for both ethnic groups.
There are not many, if any, known systems which can be used to restore cardiovascular endothelial cells which are already damaged, and Vitamin D3 can do it. "This is a very inexpensive solution to repair the cardiovascular system. We don't have to develop a new drug. We already have it."
These studies, performed at Ohio University, are the first to identify the molecular mechanism of vitamin D3-triggered restoration of the function of damaged endothelium in the cardiovasculature. While these studies were performed using a cellular model of hypertension, the implication of vitamin D3 on dysfunctional endothelium is much broader. The dysfunction of endothelium is a common denominator of several cardiovascular diseases, particularly those associated with ischemic events.
Therefore, the authors suggest that vitamin D3 may be of clinical importance in the restoration of dysfunctional cardiac endothelium after heart attack, capillary endothelium after brain ischemia (stroke), hypovolemia, vasculopathy, diabetes and atherosclerosis. This suggestion is strongly supported by several clinical studies which indicate that vitamin D3 at doses higher than those currently used for the treatment of bone diseases, may be highly beneficial for the treatment of the dysfunctional cardiovascular system.
Friday, October 13, 2017
Teens with the hearts of old men. A cautionary tale.
Kale,
parsley, broccoli, and spinach: according to new research, these leafy green
vegetables may hold even more health benefits than previously thought, as
vitamin K - found in abundance in all four - may contribute to a healthy heart.
A new study published in The Journal of
Nutrition examines the link between vitamin K levels and heart structure and functioning in young people.
Vitamin
K plays a key role in blood coagulation and bone health. Deficient levels of
the vitamin raise the risk of hemorrhage, osteoporosis, and bone fractures.
In its
dietary form, vitamin K is known as phylloquinone, or vitamin K-1. This is
abundantly found in leafy green vegetables such as kale, parsley, broccoli, spinach, iceberg
lettuce, and cabbage.
The new
research suggests that insufficient levels of the vitamin may affect the
structure of the heart, leading to a condition called left ventricular
hypertrophy (LVH).
The left
ventricle is the heart's major pumping chamber, and in LVH, this chamber is
enlarged to an unhealthy degree. As the authors of the new study explain, a
larger heart can malfunction with time, becoming less effective at pumping
blood.
LVH tends
to affect adults, but the researchers decided to study this heart structure in
young people because cardiac abnormalities that begin in childhood tend to
predict the risk of cardiovascular disease in adulthood. They found that teens
with the lowest intake of vitamin K1 from foods had triple the rate of LVH of
their counterparts who had the highest intake.
Your mom
was right…eat your greens.
Saturday, January 28, 2017
Do you know your omega-3 blood levels?
Although
regular intake of the omega-3 fatty acids, EPA and DHA is believed to have
several health benefits, some questions remain unanswered. Do we all need more
omega-3 or just some of us? Is eating fish sufficient or do we need to take
supplements? Is there a way to tell if the cells in our body are getting enough
omega-3 or if we are deficient? Yes. The Omega-3 Index may provide answers to some
of these questions.
The
Omega-3 Index reflects the relative amount of omega-3 fatty acids within red
blood cell membranes. The index can be measured using a simple blood sample. You do not need your doctor to order this test for you, it is a self administered test you can do at home. Measurements of fatty acids in red blood cell
membranes can provide important information about fatty acid intake. Recently,
the relative amount of omega-3 fatty acids in red blood cells has attracted
interest as it
may provide information about the future risk of heart disease.
Studies
show that a low Omega-3 Index is associated with increased risk of
cardiovascular disease, and it has been proposed that raising the index may
help to reduce risk.
The
Omega-3 Index reflects the relative amount of EPA + DHA in red blood cells. It
is expressed as the percentage of the total amount of fatty acids present. In
fact it’s quite simple; if 8% of all the fatty acids present in red cell
membranes is EPA+DHA, the Omega-3 Index is 8%.
The
Omega-3 Index and Cardiovascular Risk
It has
been hypothesized that the Omega-3 Index may predict the risk of future
cardiovascular events such as coronary heart disease and cardiac arrest. If
that’s correct, a low Omega-3 Index may be regarded as a risk factor, similar
to smoking, high blood pressure and high blood levels of LDL cholesterol.
The
average Omega-3 Index in the United States is believed to be between 4-5 %. In
Japan, where coronary artery disease is less common and life
span longer, the
average Omega-3 Index is 9-10%. This is because the population in Japan eats
more fish than the population in the US.
Data from
epidemiological studies and randomized controlled trials demonstrate that the
Omega-3 Index was inversely associated with the risk for mortality from coronary
heart disease. An Omega-3 Index of ≥8% was associated with the greatest
protection, whereas an index of ≤4% was associated with the least.
Another
study, published 2008 showed that the Omega-3 Index as independently associated
with the risk of developing acute coronary syndrome.
An Omega-3
Index >8% is optimal while an index of <4% may be regarded as deficient.
The
simplest way to improve the Omega-3 Index is to increase your intake of EPA and
DHA by eating marine products rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
Recommendations
For the Intake of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
For people
without cardiovascular disease, most experts recommend eating a variety of fish
(preferably oily) at least twice a week to maintain a mean intake of 4-500 mg
of EPA+DHA daily.
For those
with documented coronary heart disease, a daily dose of EPA+DHA of 1.000 mg per
day is recommended.
For
someone wanting to achieve the suggested ideal Omega-3 Index of 8% 2000 mg of
EPA + DHA daily is suggested.
Finally for
individuals with elevated serum triglycerides a daily dose of EPA + DHA of 2000
mg to 4000 mg per day is what doctors suggest. Since fish may be contaminated
with mercury and other pollutants, be sure the fish oil supplement you choose
is purified and has been third party tested.
IFOS, The InternationalFish Oil Standards program offers consumers a way to compare the highest
quality fish oil brands. Carlson offers a wide array of potent pure fish oil
supplements that have been tested by IFOS.
Labels:
DHA,
EPA,
Fish Oil,
Healthy Heart,
Omega 3's,
Prevention
Friday, December 16, 2016
Want to really improve your chances of preventing heart disease?
Learn how lifestyle factors cut your risk. Here
they are:
2. Not being obese
(having a B.M.I. less than 30)
3. Performing physical activity at least once a
week.
4. Having a healthful diet pattern.
Here is what defines a healthful diet pattern. Do
at least half of these things: eat more fruits, nuts, vegetables, whole grains,
fish and dairy products; eat less processed meats, unprocessed red meats, sugar
sweetened beverages, trans fats and sodium.
Every one of the four lifestyle factors was
associated with a decreased risk of coronary events.
That’s the first bit of good news. Doing any one of these things makes a difference.
But the effect is cumulative. The researchers
divided people into three groups based on these factors. “Favorable” required
at least three of the four factors, “intermediate” required two of them, and
“unfavorable” required one or none. Across all studies, those with an
unfavorable lifestyle had a risk that was 71 percent to 121 percent higher than
those with a favorable lifestyle.
More impressive was the reduction in coronary
events — heart attacks, bypass procedures and death from cardiovascular causes
— at every level of risk. Those with a favorable lifestyle, compared with those
with an unfavorable lifestyle, had a 45 percent reduction in coronary events
among those at low genetic risk, a 47 percent reduction among those with
intermediate genetic risk, and a 46 percent reduction among those at high
genetic risk.
What does this mean in real-world numbers? Among
those at high genetic risk in the oldest cohort study, 10.7 percent could
expect to have a coronary event over a 10-year period if they had an
unfavorable lifestyle. That number was reduced to 5.1 percent if they had a
favorable lifestyle. Among those at low genetic risk, the 10-year event rate
was 5.8 percent with an unfavorable lifestyle and 3.1 percent with a favorable
lifestyle. In the other cohort studies, similar relative reductions were seen.
These differences aren’t small. The risk of a
coronary event in 10 years was halved. The absolute reduction, more than 5
percentage points in the genetic group at high risk, means that lifestyle
changes are as powerful as, if not more powerful than, many drugs we recommend
and pay billions of dollars for all the time.
There are important lessons to be learned. These
results should encourage us that genetics do not determine everything about our
health. Changes in lifestyle can overcome much of the risk our DNA imposes.
Lifestyle changes are hugely important not only
for those at low risk, but for those at high risk. The relative reductions in events
were similar at all levels of genetic risk.
Remember that changes in lifestyle also reduce your
risk of cancer, the number two killer making it clear that a healthy lifestyle
has implications for an even greater number of us!
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)